The socket welds applications are quite important in the piping and manufacturing industries as they offer a strong joint to the piping industry particularly to the small sized pipes. In this article, you will learn all that you need to know about socket welds; the application as well as the types of socket weld. These welds are preferred for use in high pressure gadget since we understand their difference from other welds.
What is a Socket Weld?
A socket weld is a kind of weld that connects chiefly to small diameter pipe since incidences that require the use of this method must be very accurate and strong. The term “Socket Weld” defines how the pipe fits into a little indentation in the joint (or the “socket” of the joint). One pipe fits into this other pipe’s socket and the joint is completed by welding at the outer surface. This technique provides the user with a strong and sealed connection that is appropriate for use in applications that may require high pressures or elevated temperatures.
Flange and socket welds are most suitable for industries such as petrochemical, oil and gas and water industries because of the nature and service they provide.

What Kind of the Weld is a SW?
The Socket Weld has no stress relief at the weld joint because it is a filet type of weld, and welding is done only around the joint of the pipe. This makes it different from butt welds that comprise welding ends of the pipes through their thickness. To a certain extent socket welds have the advantage of filet weld around the socket connection and are far less likely to leak or fail when under critical conditions.
Socket welds are easy to install and less expensive to perform as compared to other types of welds because there is no requirement of chamfering of the edges.
Why Are Socket Welds Used?
Socket Welds are even more handy because of their ability to offer maximum power and no leakage. They provide a very powerful and rigid connection with minimal likelihood of further movement making them suitable for use in a system that demands that the pipes have thin cross-sectional dimensions and that work at high pressures. Here are some of the key reasons socket welds are preferred:
High-Pressure Capability: Fillet welds are ideal for use on systems that need high pressure containment since the weld offers a lot of strength.
Ease of Installation: Thus, socket welds enable the employment of a basic procedure for their preparation and thus can be made in a mere short time and without calling in reinforcements.
Strong, Leak-Resistant Joint: In operations where leakage is undesirable, the design of socket welds minimizes the chances of leakage occurring.
This is why it is common to find application of socket welds in industries that require assurance of non-running in case the weld collapses.
Types of Socket Weld Fittings
Therefore, socket welds are not fixed; they are of different types depending on the type of pipe connection required. Let’s look at some common types:
Socket Weld Elbows
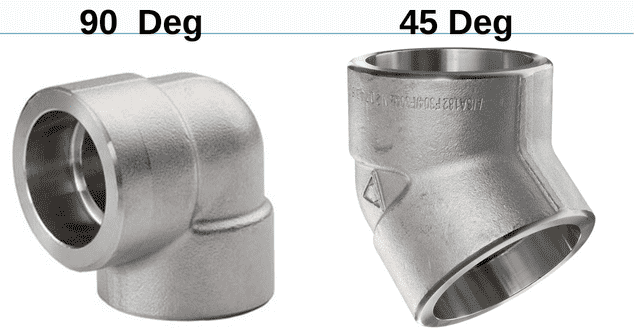
Socket Weld Elbows are used to provide turns or changes in direction of the flow of fluids in a system. It is available in 90° and 45° and enables designers to route adjustments while adhering to the system design.
Socket Weld Tees
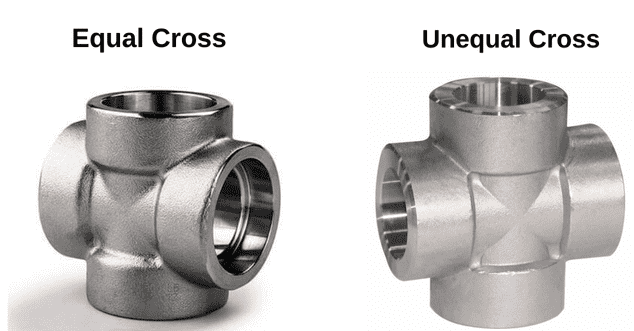
A Socket Weld Tee connects three pipes forming the tee configuration of pipe to be suitable to incorporate branch pipe from the main pipe. Other types are Equal Cross and Unequal Cross; there are also flexibility of flow management associated with this layouts.
Socket Weld Couplings
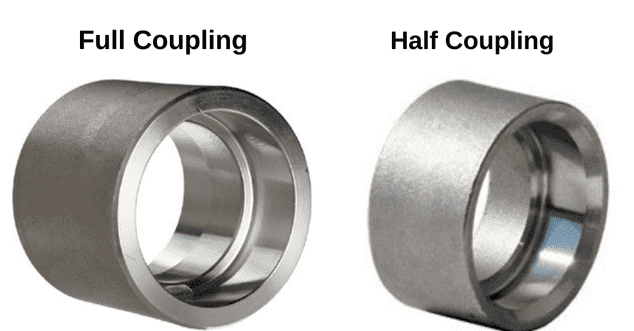
There are joint types that join two pipes one after another end to end. Two basic configurations of coupler types are Full-Coupling and Half-Coupling type, based on whether both ends of the coupling are socket welded or only one end respectively.
Socket Weld Reducers
Socket Weld Reducers are used to join pipes of dissimilar size. They are very essential in control of flow rates in a given piping system and especially where pipes are of different sizes.

What is the Role or Purpose of SW?
Socket welds are used in conditions that need high tensile strength and no leakage but the pipes are small in size. Their applications span various industries:
Petrochemical: Pipe socket welds are used to connect pipes in refineries when high pressure is required in a system.
Power Generation: In circulation systems and power plant tubes, socket welds are useful in joining highly pressurized small diameter pipes.
Water Treatment: The features such as high strength and absence of leakage make socket welds suitable for piping in water and wastewater treatment companies.
Socket welds are used where pipework is required to be only a certain size but requires a high standard of safety and efficiency.
Pros and Cons of Socket Welds
To give a complete picture, let’s look at some advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages:
- Strong and durable
- Leak-resistant
- Advantageous for getting small diameter pipe and also cost effective.
- Little pre-installation work wants to develop
Disadvantages:
- The method is preferably carried out on pipes with wall thickness 10 dividers or less of the inner pipe diameter.
- Most of the growth and shrinkage under heat puts some stress
- Fillet weld might take time in order to produce even cover and strength.
Final Thoughts
Socket welds are the most important link in industrial piping where it is most liked because it provides maximum Leak-Proof, Quick assembly. Regarding the applicability for small diameter, high pressure pipe systems, SW is usually most often met, because this type of connection provides high strength, simplicity and reliability for the application. In this manner, it is possible to decipher the different kinds of socket welds that are available in the market, hence, come up with an efficient way on what works best in the industry.




